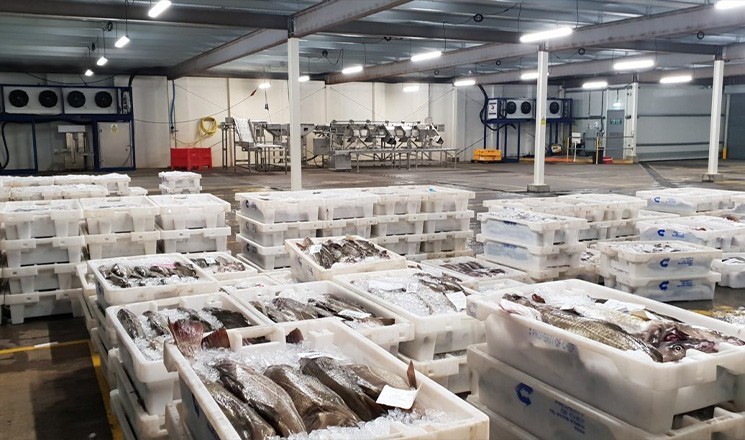
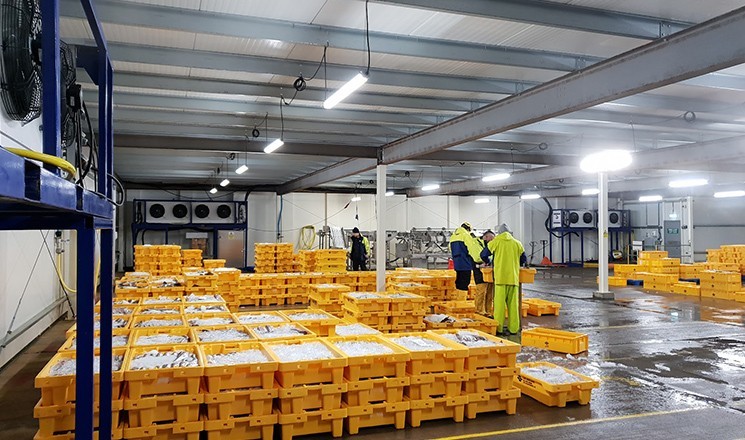
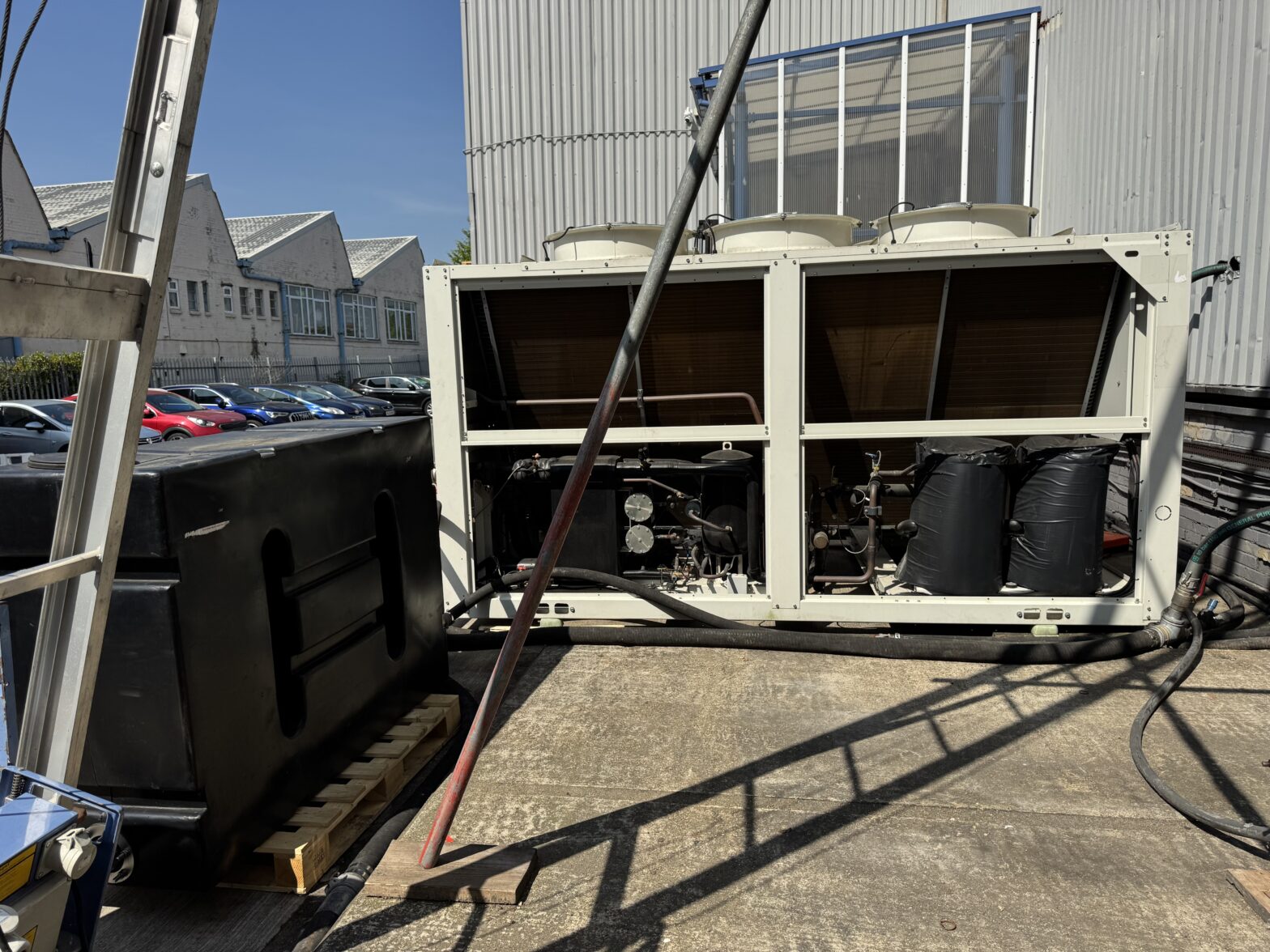
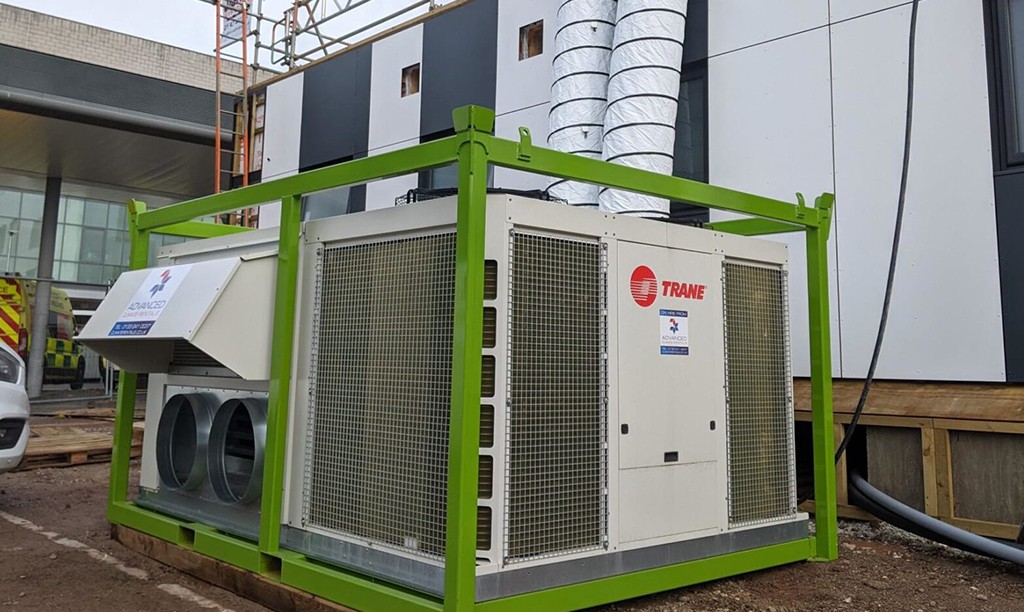
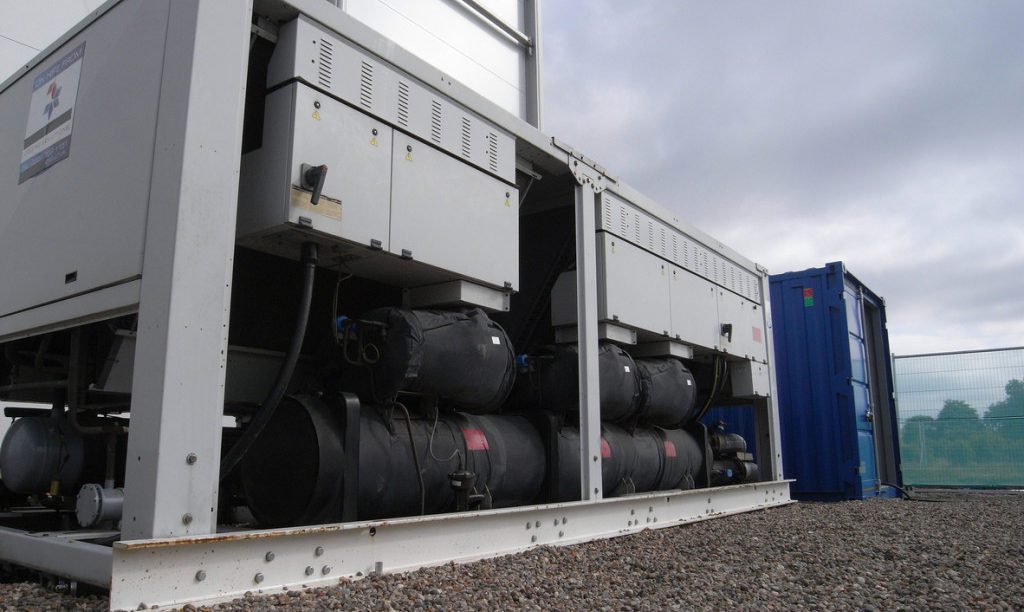
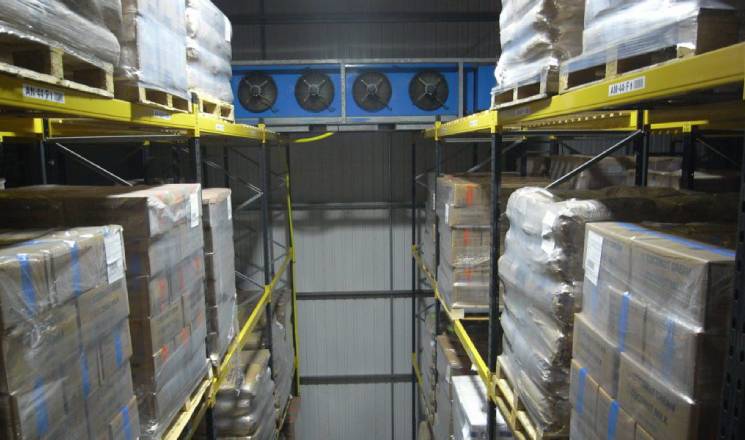
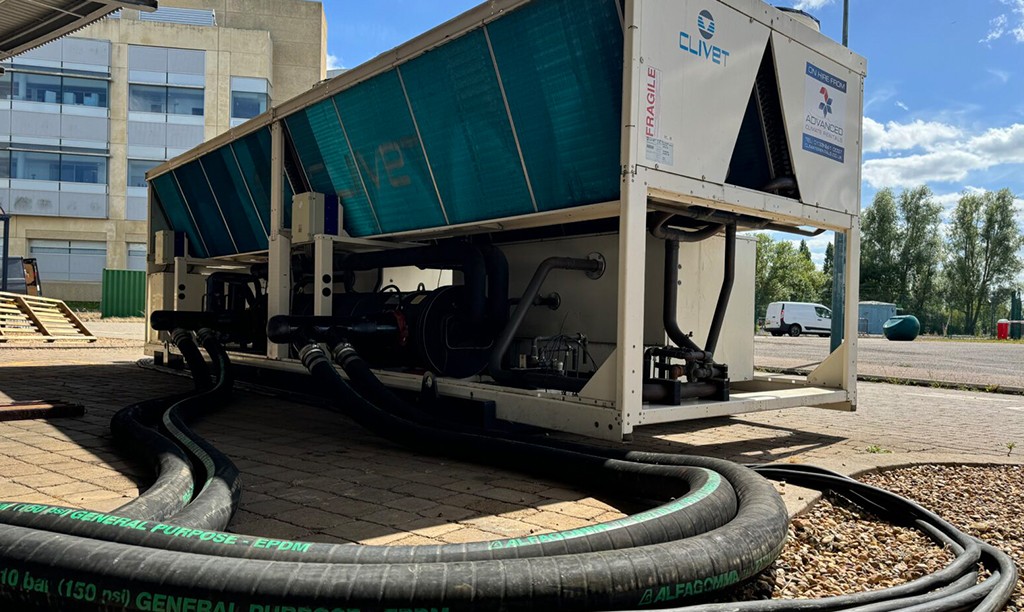
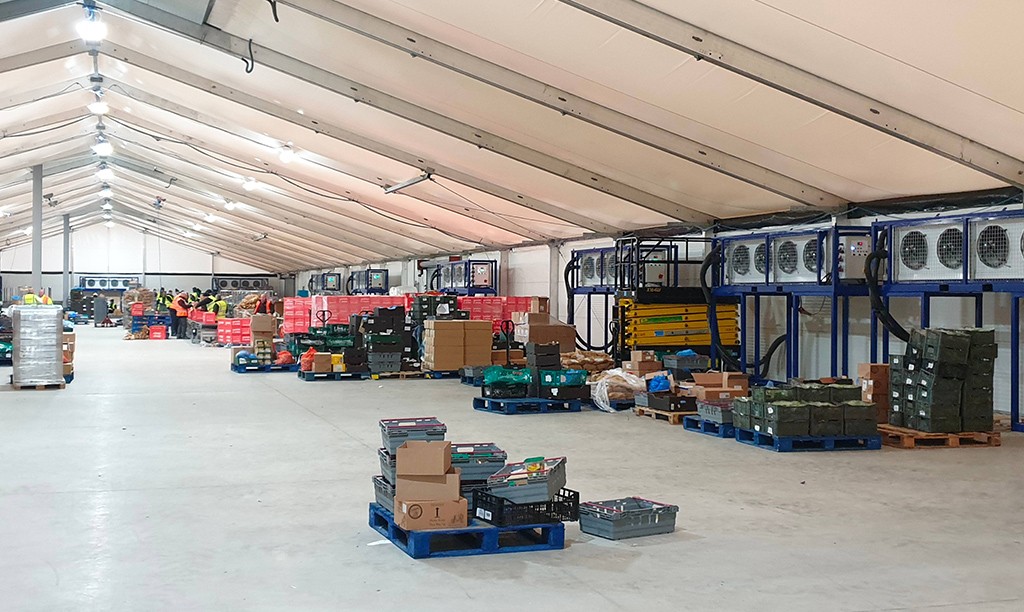
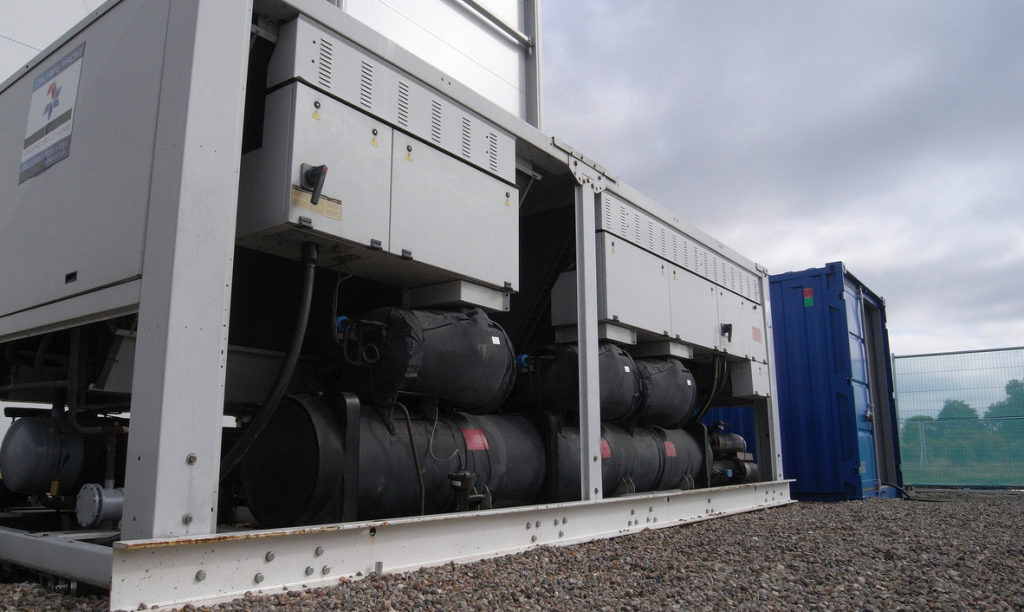
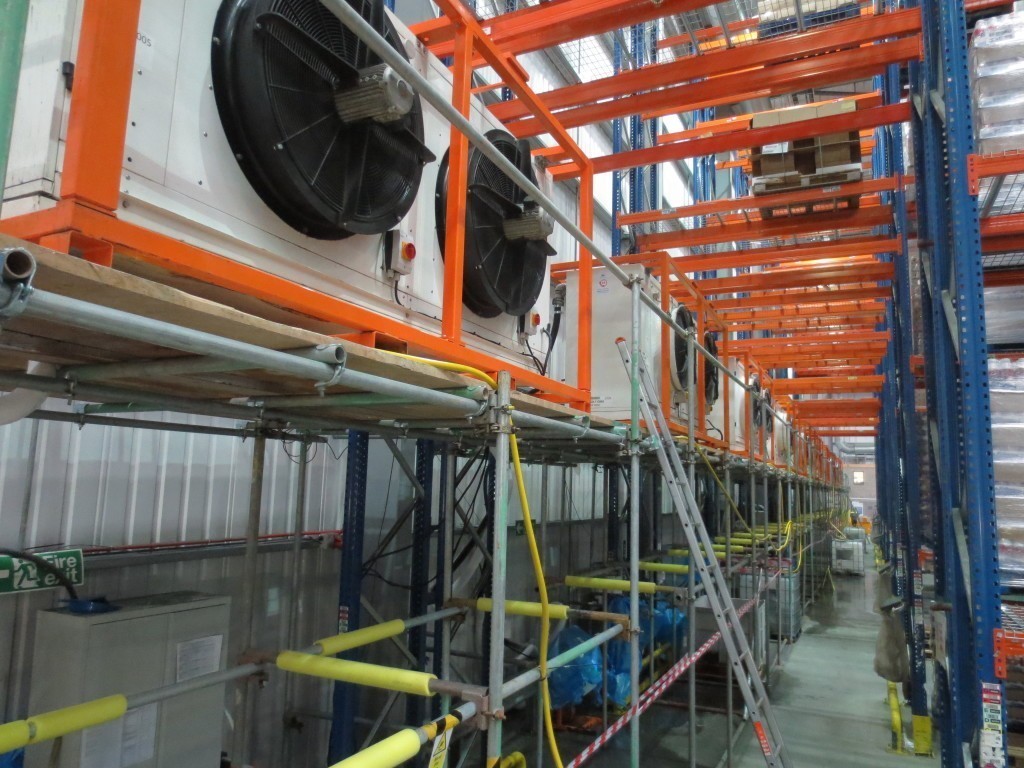
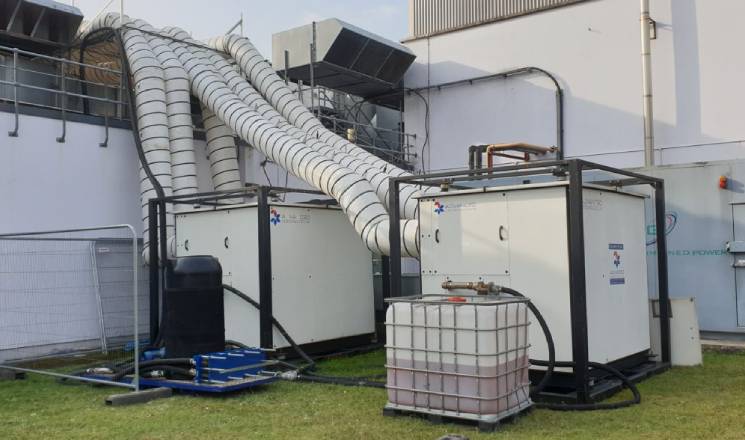
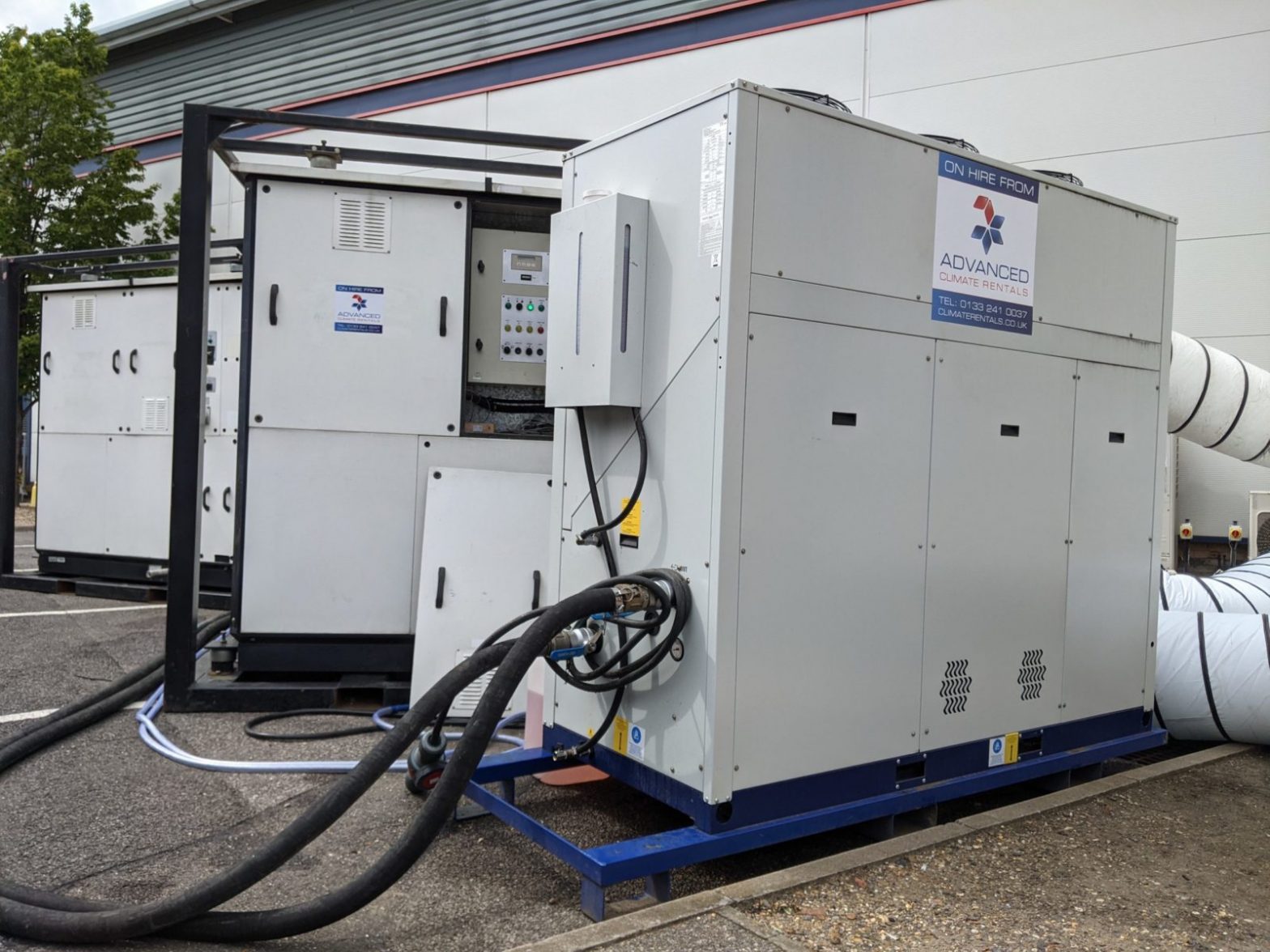
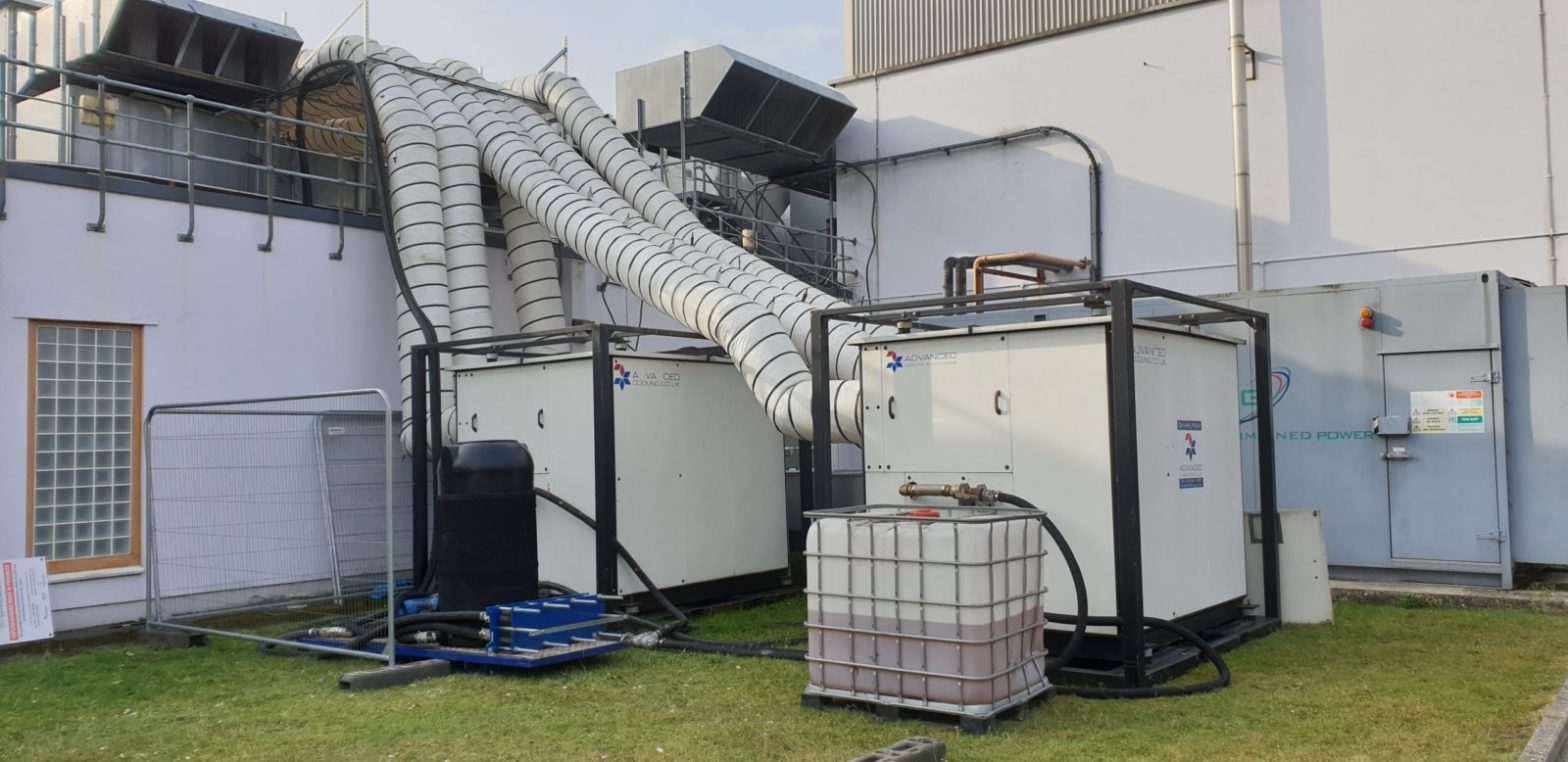
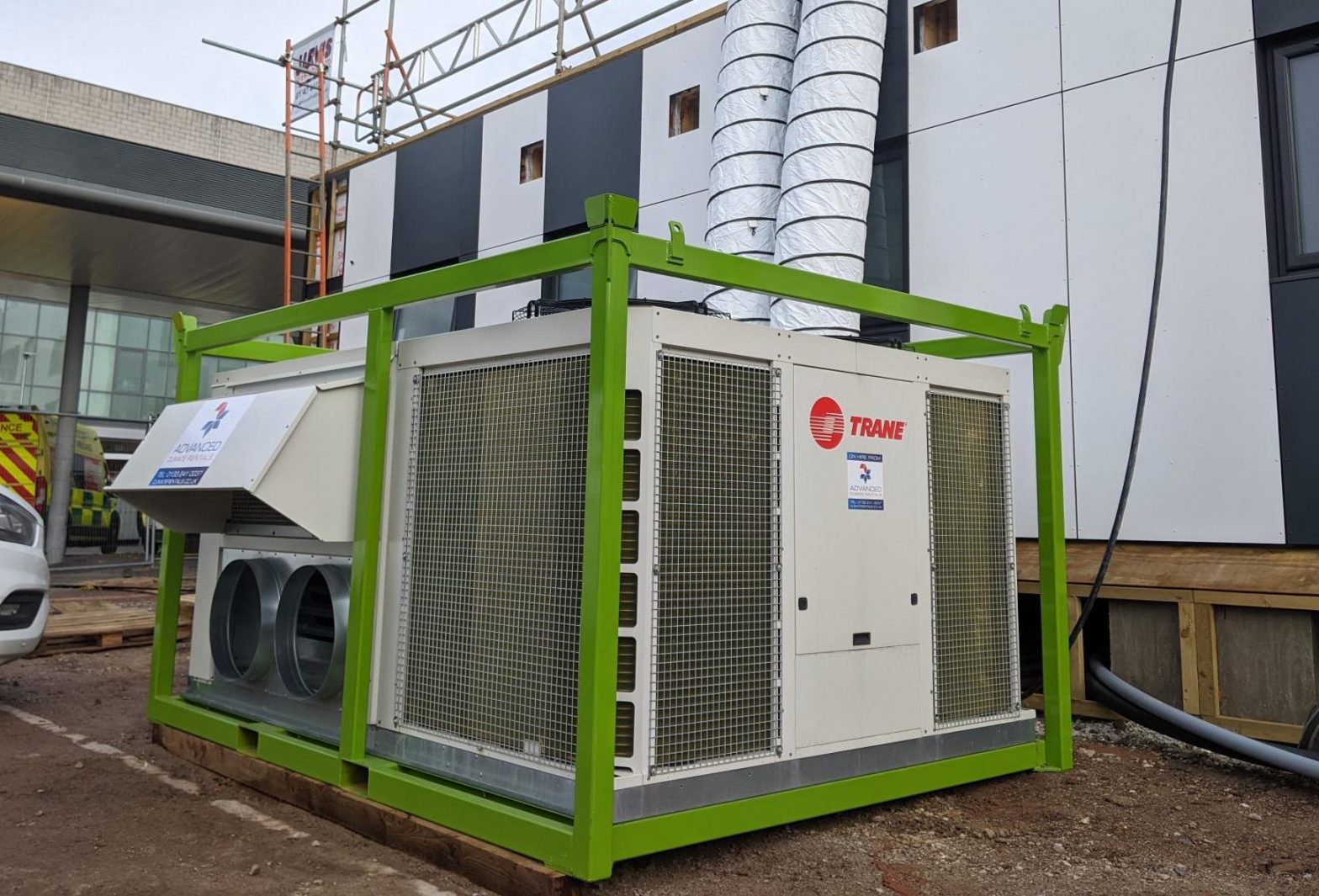
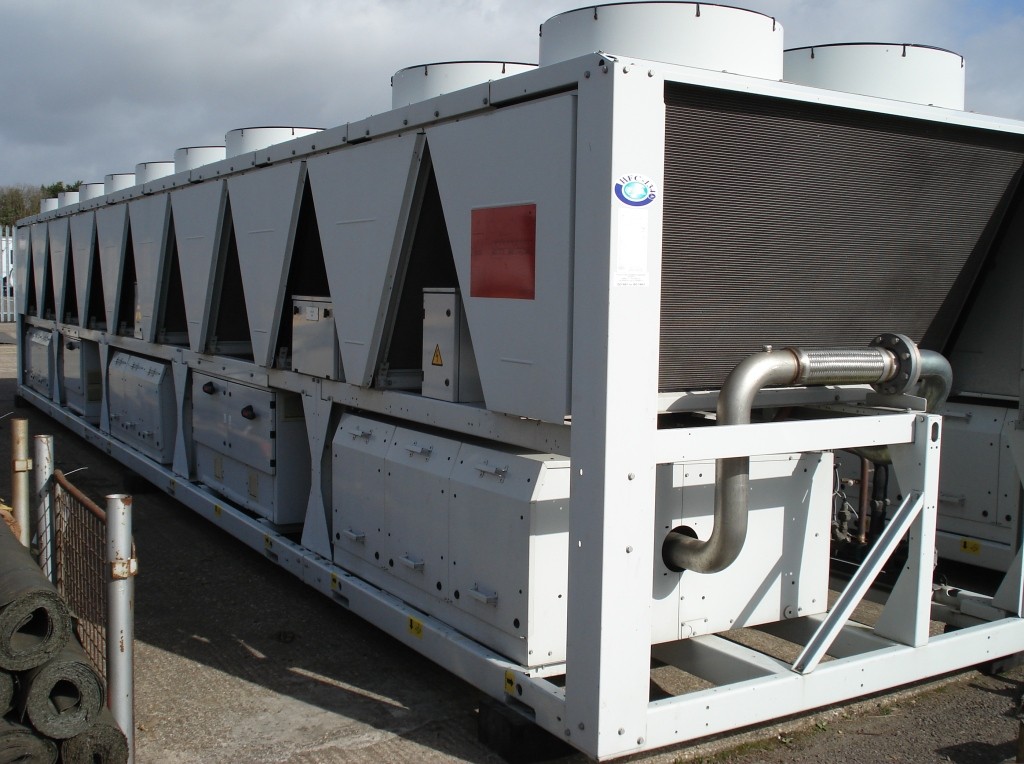
Probably the most efficient cooling systems available use Ammonia refrigerant.
Pumped around a warehouse in steel pipework loop, it is used in a piece of equipment called an evaporator to cool the space before returning to the compressor plant and starting the circuit again.
Whilst Ammonia (NH3) is very efficient, plant can be expensive to service. Also, leaks are dangerous to health, so highly specialist engineering services are required.
Leaving aside Ammonia’s health and safety challenges, its other major advantages include a GWP (global warming potential) rating of zero, also, its common place in nature means it is readily re-absorbed without contamination.